If you’ve ever typed a few sentences into an AI tool, clicked “Generate,” and watched a full video appear, you probably felt like you’d just witnessed magic. One minute you’re staring at plain text, the next minute there are moving images, transitions, music, and sometimes even voice-overs.
Most people use text to video AI without really understanding what’s happening behind the scenes. And that’s okay—you don’t need to be technical to use it well. But once you do understand how it works, your results get noticeably better.
In this guide, I’ll break everything down in plain English. No jargon. No coding talk. Just a clear explanation of how AI turns prompts into videos, why some prompts look amazing while others flop, and how you can improve your results even if you’re a complete beginner.
Table of Contents
What Happens After You Enter a Prompt
When you type a prompt into a text to video AI tool, a lot happens in just a few seconds. It feels instant, but under the hood, the AI is doing multiple jobs at once.
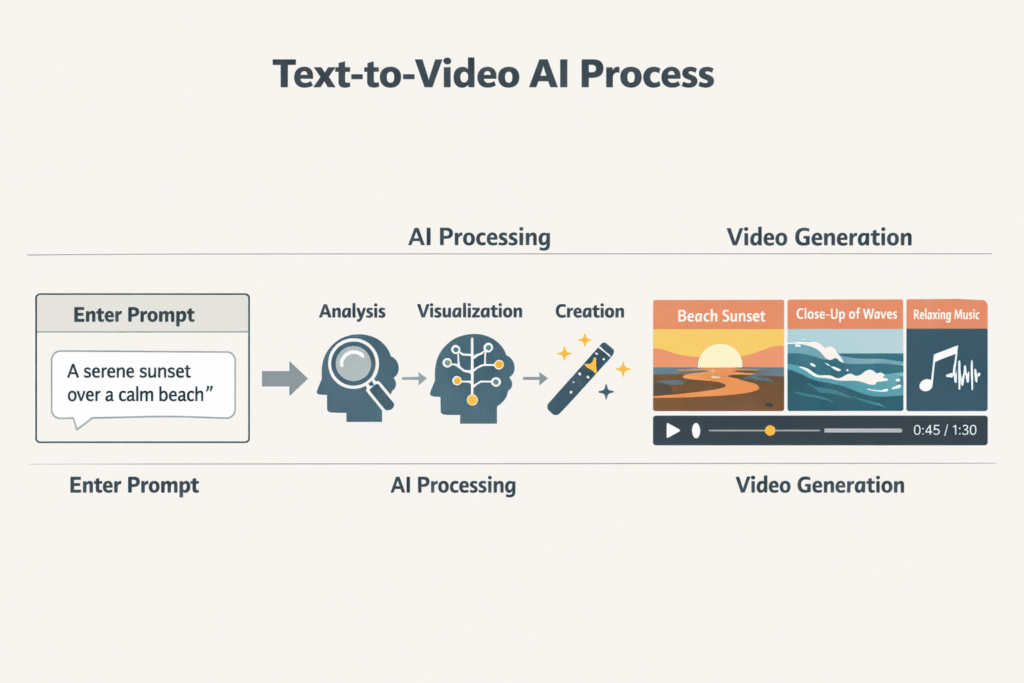
Step 1: The AI Reads Your Prompt Like a Story
The first thing the AI does is interpret meaning. It doesn’t read your prompt like a human does, but it tries to understand:
- What is happening?
- Who or what is involved?
- What mood or tone is implied?
- Is this realistic, cinematic, animated, calm, dramatic, or fast-paced?
For example,
“A peaceful sunrise over a quiet village with soft music”
signals calm visuals, warm lighting, slow motion, and gentle transitions.
Meanwhile,
“A fast-paced tech startup montage with futuristic visuals”
tells the AI to think energy, motion, sharp cuts, and modern aesthetics.
Step 2: Your Text Is Broken Into Visual Concepts
Next, the AI splits your prompt into visual ideas. It identifies keywords that can be translated into images or motion, such as:
- Objects (hands, buildings, laptops, nature)
- Actions (walking, breaking, rising, flowing)
- Styles (cinematic, animated, realistic, watercolor)
- Emotions (hopeful, dark, inspiring)
This is why vague prompts often produce random results—the AI doesn’t have enough clear visual anchors to work with.
Step 3: The AI Searches Its Learned Visual Patterns
Text to video AI doesn’t “record” videos from scratch. Instead, it uses massive datasets of visual patterns it has learned during training. It predicts what visuals should look like based on your words.
Think of it as an extremely advanced autocomplete—but for video.
If millions of examples link “sunrise” with orange skies and silhouettes, that’s what the AI will lean toward.
Step 4: Scenes Are Generated and Stitched Together
Once visuals are predicted, the AI generates short clips or frames, then stitches them into scenes. Some tools:
- Automatically add transitions
- Match visuals to background music
- Adjust pacing based on tone
- Add captions or motion text
This is where text to video AI really shines for creators who don’t want to edit manually.
Step 5: Final Styling and Rendering
Finally, the video is rendered based on the platform’s preset styles. Some tools favor:
- Stock-video realism
- AI-generated imagery
- Slideshow-style motion
- Cinematic storytelling
The style depends heavily on the tool you’re using—and how specific your prompt is.
Why Some Prompts Work Better Than Others
If you’ve ever wondered why one prompt gives you a stunning video while another looks awkward or off-target, the reason usually comes down to structure.
Clarity Beats Creativity (At First)
A common beginner mistake is trying to be poetic instead of clear.
For example:
“The soul journeys through time and hope”
Sounds deep, but visually? Very unclear.
Compare that to:
“A lone traveler walking through a desert at sunset, symbolizing hope and endurance”
Same idea—but now the AI has something concrete to work with.
Simple Structure That Works
You don’t need a complex formula. This simple structure is enough for most text to video AI tools:
Scene + Action + Style + Mood
Example:
“A person standing on a mountain peak, wind blowing, cinematic style, inspirational mood”
That single sentence gives the AI direction without overwhelming it.
One Prompt ≠ One Scene (Always)
Many tools automatically break a prompt into multiple scenes. If your prompt jumps between ideas too fast, the video may feel messy.
Bad example:
“A city at night, then a beach, then a child laughing, then futuristic robots”
Better approach:
Focus on one theme or story per video—or clearly separate scenes if the tool allows it.
Visual Interpretation Limits
Here’s the honest truth: text to video AI is powerful, but it’s not perfect. Understanding its limits will save you frustration.
AI Is Literal, Not Imaginative
Humans read between the lines. AI usually doesn’t.
If you say:
“Freedom breaking through chains”
You might imagine symbolism, emotion, and depth.
The AI might literally show chains snapping—sometimes awkwardly.
This doesn’t mean it’s bad. It just means you need to guide it.
Abstract Concepts Are Harder
AI struggles most with:
- Deep metaphors
- Complex emotions
- Spiritual or philosophical ideas
- Cultural symbolism without visuals
That’s why many creators convert abstract ideas into physical visuals.
Instead of:
“Inner healing”
Try:
“A calm person sitting by a lake at sunrise, breathing peacefully”
Consistency Can Be a Challenge
Another limitation is character consistency. The same “person” may look slightly different across scenes unless the tool specializes in character locking.
This is normal behavior for most text to video AI platforms today.
How to Improve Results Without Technical Skills
You don’t need editing experience, design skills, or AI knowledge to get better results. Small tweaks make a big difference.
Be Descriptive, Not Long
Long prompts don’t always mean better prompts. Clear, visual language matters more than word count.
Instead of writing a paragraph, write one or two strong sentences packed with visuals.
Use Visual Adjectives
Words like these help a lot:
- Soft lighting
- Slow motion
- Cinematic
- Close-up
- Wide shot
- Minimalist
- Warm tones
- Dark background
These guide how the video feels, not just what appears.
Match Prompt Style to Your Platform
If you’re creating content for:
- YouTube Shorts / TikTok → Fast pacing, bold visuals
- Meditation or healing videos → Slow motion, calm scenes
- Marketing videos → Clean visuals, modern style
- Educational content → Clear scenes, readable text
Text to video AI responds better when the intent is obvious.
Generate, Review, Regenerate
Almost no one gets a perfect result on the first try. The real power of text to video AI is iteration.
Change one thing at a time:
- Add “cinematic”
- Remove vague words
- Focus on one scene
- Adjust mood
Each generation teaches you how the tool “thinks.”
Use Built-In Templates When Available
Many platforms offer templates for social media, ads, or storytelling. These are not cheating—they’re shortcuts trained to perform well.
For beginners, templates + good prompts = surprisingly professional videos.
Common Text to Video AI Tools
If you’re wondering where all this actually happens, the good news is that you don’t need obscure or complicated software. Many popular platforms already use text to video AI behind the scenes, each with its own strengths depending on what you want to create.
CapCut
CapCut is one of the most beginner-friendly text to video AI tools out there. It allows you to turn simple prompts or scripts into short-form videos, especially for TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts.
Its biggest advantage is how well it combines AI-generated visuals with automatic captions, music, and transitions, making it perfect for creators who want fast results without manual editing.
Want to see how CapCut turns simple text into scroll-stopping videos? You can try CapCut here and explore its text-to-video features for yourself.
Canva
Canva has quietly become a powerful text to video AI option, especially for non-technical users. With its Magic Design and text-to-video features, you can paste a short prompt or script and instantly get a polished video layout with scenes, animations, stock footage, text overlays, and music.
It’s ideal for social media videos, presentations, and brand-friendly content where clean visuals and consistency matter more than cinematic effects.
VideoExpress AI
VideoExpress AI focuses more on prompt-driven storytelling. You enter a detailed text description, and the tool generates scene-based videos that feel more cinematic.
It’s popular among creators making motivational content, explainer videos, and faith-based or storytelling videos because it handles pacing and visuals in a more narrative way.
If you’re curious how prompt-based storytelling works in real time, you can try VideoExpress AI here and generate your first video in minutes.
Pictory
Pictory is designed for turning scripts and blog posts into videos. Instead of generating everything from scratch, it uses AI to match your text with relevant visuals, stock footage, and captions. This makes it a strong option for bloggers, educators, and marketers repurposing written content into video format.
InVideo AI
InVideo AI blends text to video AI with customizable templates. You describe what you want, and the platform builds a draft video complete with scenes, voice-over suggestions, and background music.
It’s especially useful for promotional videos, ads, and YouTube content where structure matters.
If you want structured, ready-made video drafts from a single prompt, you can try InVideo AI here and test its AI video workflow.
Runway
Runway is more advanced and creative-focused. Its text to video AI features allow users to generate artistic and experimental visuals directly from prompts. While it has a slightly higher learning curve, it’s powerful for creators who want stylized, cinematic, or abstract video outputs.
Synthesia
Synthesia takes a different approach by combining text to video AI with AI avatars. Instead of abstract visuals, it turns scripts into presenter-style videos where a digital human speaks your text. This is widely used for training videos, corporate communication, and educational content.
Conclusion
Text to video AI isn’t magic—but it’s close enough to feel like it. What really happens is a smart system translating your words into visual predictions based on patterns it has learned.
Once you understand how prompts are interpreted, why structure matters, and where AI has limits, everything clicks. You stop blaming the tool and start working with it.
The best part? You don’t need technical skills to improve. Just clearer prompts, better expectations, and a little experimentation. As text to video AI tools continue to evolve, the gap between imagination and creation keeps shrinking—and that’s exciting for creators at every level.
FAQs
What is text to video AI?
Text to video AI is a technology that converts written prompts into videos by generating visuals, motion, and sometimes audio based on your text input.
Why does my AI video not match my prompt?
This usually happens when prompts are too vague, abstract, or overloaded with ideas. AI works best with clear, visual instructions.
Do I need editing skills to use text to video AI?
No. Most text to video AI tools are designed for beginners and handle editing automatically.
Can text to video AI replace video editors?
Not completely. It’s best for quick content, storytelling, and ideation. Human editors still excel at complex narratives and fine details.
How can I get better results from text to video AI?
Use clear visual language, focus on one idea per prompt, add style and mood descriptors, and iterate by regenerating videos with small changes.